General waste management involves the collection, transportation, and disposal of everyday waste materials. Effective waste management minimizes environmental impact and promotes sustainability.
Proper waste management is essential for maintaining a clean and healthy environment. It involves several processes, including waste collection, transportation, processing, and disposal. Efficient waste management systems help reduce pollution, conserve natural resources, and support public health. Recycling and composting are crucial components that divert waste from landfills and promote resource recovery.
Communities and businesses must adopt sustainable practices to manage waste responsibly. By implementing effective strategies, we can minimize the negative effects of waste on our planet and ensure a sustainable future for generations to come. Educating the public about waste reduction and recycling is vital for achieving these goals.
The Crisis Of Modern Waste
The world faces a growing crisis of modern waste. Every day, we generate tons of trash. This trash impacts our planet, health, and future. Effective waste management is urgent.
Global Impact
Modern waste affects the entire globe. Plastic pollution harms oceans and wildlife. Landfills release harmful gases. These gases contribute to climate change. Poor waste management leads to soil and water contamination. This affects our food and health.
Developing countries suffer the most. They lack proper waste disposal systems. This leads to waste piling up in streets and rivers. Rich countries export waste to poorer ones. This creates a global imbalance and ethical issues.
Statistics At A Glance
Here are some staggering statistics about modern waste:
- About 2 billion tons of waste are generated each year.
- Only 16% of waste is recycled globally.
- Plastic waste in oceans could triple by 2040.
- Landfills account for 11% of global methane emissions.
Below is a table highlighting more waste statistics:
| Category | Amount (tons/year) | Recycling Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Plastic Waste | 300 million | 9% |
| Food Waste | 1.3 billion | 25% |
| Electronic Waste | 50 million | 20% |
| Paper Waste | 400 million | 68% |
These numbers show the urgent need for better waste management.
Credit: www.sketchbubble.com
Types Of Waste
Understanding the types of waste is crucial for effective waste management. Different waste types require different handling and disposal methods. Let's explore the various categories of waste.
Household Vs. Industrial
Household waste includes everyday items discarded by homes. This includes food scraps, paper, plastics, and glass. Proper segregation and disposal help in recycling and reducing landfill use.
Industrial waste comes from factories and industries. It includes chemicals, metals, and manufacturing by-products. Industrial waste often requires special handling to prevent environmental harm.
Hazardous Vs. Non-hazardous
Hazardous waste contains substances that can be dangerous. Examples include batteries, pesticides, and medical waste. Proper disposal is vital to avoid health and environmental risks.
Non-hazardous waste is not immediately dangerous. Examples include food waste, paper, and plastic. Proper recycling and composting can manage non-hazardous waste efficiently.
| Waste Type | Examples | Handling Method |
|---|---|---|
| Household Waste | Food scraps, paper, plastics | Segregation, recycling |
| Industrial Waste | Chemicals, metals | Special handling, treatment |
| Hazardous Waste | Batteries, pesticides | Safe disposal, containment |
| Non-Hazardous Waste | Food waste, paper | Recycling, composting |
Principles Of Eco-smart General Waste Management
Eco-smart General waste management focuses on minimizing waste impact. This involves smart strategies to handle waste effectively. It promotes a cleaner and healthier environment.
Reduce
Reducing waste means creating less waste from the start. Buy products with less packaging. Choose items that last longer. Use digital files instead of paper. These actions help reduce waste significantly.
Reuse
Reusing items extends their lifecycle. Donate clothes you no longer wear. Repurpose glass jars as storage containers. Use both sides of paper before recycling. Reusing helps save resources and energy.
Recycle
Recycling turns waste into new products. Sort your waste into categories: paper, plastic, glass, and metal. Use local recycling bins. Recycling conserves raw materials and reduces pollution.
Energy Recovery
Energy recovery converts waste into usable energy. This process includes waste-to-energy plants. They burn waste to produce electricity. Energy recovery reduces landfill use. It also creates renewable energy.
| Principle | Action |
|---|---|
| Reduce | Buy long-lasting products, use digital files |
| Reuse | Donate, repurpose, use both sides of paper |
| Recycle | Sort waste, use recycling bins |
| Energy Recovery | Convert waste to energy, reduce landfill use |

Credit: stock.adobe.com
Innovative Recycling Techniques
Recycling has come a long way from simple sorting of materials. Innovative recycling techniques have emerged, pushing boundaries and redefining waste management. These advanced methods not only reduce landfill waste but also provide new resources. Let's explore two such techniques: Upcycling and Bioconversion.
Upcycling
Upcycling transforms waste materials into new, high-quality products. This process adds value to discarded items.
- Old furniture becomes stylish home decor.
- Used tires are crafted into playground surfaces.
- Plastic bottles transform into eco-friendly clothing.
Upcycling reduces the need for raw materials. This conserves resources and reduces pollution. It also encourages creativity and innovation. Many artists and designers now focus on upcycled products.
Bioconversion
Bioconversion involves turning organic waste into useful products. This technique uses natural processes like composting and fermentation.
| Type of Waste | End Product |
|---|---|
| Food scraps | Compost |
| Animal manure | Biogas |
| Wood chips | Bio-oil |
Bioconversion helps in managing organic waste efficiently. It also produces valuable by-products. This method is eco-friendly and sustainable. It reduces greenhouse gas emissions and improves soil health.
Both upcycling and bioconversion are vital in modern waste management. They offer innovative solutions for reducing waste and protecting the environment.
Composting: Nature's Recycling
Composting is a natural way to recycle waste. It turns organic materials into nutrient-rich soil. This process helps the environment and reduces waste. Let's explore the benefits and how to start composting.
Benefits
- Reduces Landfill Waste: Composting keeps waste out of landfills.
- Enriches Soil: Compost adds nutrients to the soil.
- Saves Money: You spend less on fertilizers.
- Decreases Methane Emissions: Less waste in landfills means less methane gas.
- Improves Soil Health: Compost helps soil retain moisture.
How To Start
- Choose a Location: Pick a spot in your yard for the compost pile.
- Get a Bin: Use a compost bin to contain the waste.
- Add Organic Waste: Add fruit peels, vegetable scraps, and coffee grounds.
- Balance Green and Brown: Mix green waste with brown materials like leaves.
- Turn the Pile: Stir the compost every few weeks to add air.
- Keep it Moist: Water the pile to keep it damp, not wet.
- Wait and Use: In a few months, you'll have rich compost for your garden.
| Green Materials | Brown Materials |
|---|---|
| Fruit Peels | Dry Leaves |
| Vegetable Scraps | Cardboard |
| Coffee Grounds | Newspaper |
Composting is easy and beneficial. Start composting today and help nature recycle.
Technology In General Waste Management
Technology is transforming waste management. It makes the process efficient and sustainable. New tools and methods help reduce waste, recycle more, and save resources.
Smart Bins
Smart bins are a game changer in waste management. These bins use sensors to monitor waste levels. They send alerts when they need emptying. This reduces unnecessary trips and saves fuel.
Smart bins also help with recycling. They can sort waste into different categories. This makes recycling easier and more effective.
- Reduce fuel costs
- Monitor waste levels
- Improve recycling rates
Waste To Energy
Waste to energy technology turns waste into electricity. This reduces landfill use and provides a renewable energy source. The process involves burning waste to produce steam. This steam drives turbines to generate electricity.
There are several benefits to waste to energy:
- Reduces landfill waste
- Produces renewable energy
- Decreases greenhouse gases
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduces landfill waste | Less waste goes to landfills. |
| Produces renewable energy | Converts waste into electricity. |
| Decreases greenhouse gases | Less methane from landfills. |
Community Involvement
Community involvement plays a vital role in general waste management. By working together, communities can significantly reduce waste. They can also promote sustainable practices. Active participation leads to cleaner and healthier environments.
Local Initiatives
Local initiatives have a significant impact on waste management. Neighborhoods can organize regular clean-up drives. These drives remove litter from public spaces.
- Organize monthly clean-up events
- Set up recycling stations in public areas
- Promote composting in community gardens
Engaging local businesses is also crucial. They can support waste reduction by minimizing packaging. They can also donate surplus food to shelters.
Education And Awareness
Education and awareness are essential for effective waste management. Schools can integrate waste management topics into their curriculum. This teaches children the importance of recycling and reducing waste.
- Organize workshops on waste segregation
- Distribute informative pamphlets
- Use social media to spread awareness
Community centers can hold informative sessions. These sessions teach residents about the benefits of proper waste disposal. Visual aids and hands-on activities make learning engaging.
| Action | Impact |
|---|---|
| Monthly clean-up events | Cleaner neighborhoods |
| Recycling stations | Reduced landfill waste |
| Composting | Less organic waste |
By focusing on these areas, communities can make a significant difference. They can ensure a greener future for everyone.

Credit: www.creativesafetysupply.com
Future Of Waste Management
The future of waste management is evolving rapidly. New technologies and policies are shaping a more sustainable world. Let's explore what's coming next.
Policy Changes
Governments are creating new policies to manage waste effectively. These policies aim to reduce waste and increase recycling.
| Policy | Description |
|---|---|
| Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) | Producers are responsible for recycling their products. |
| Zero Waste Policies | Goals to eliminate all waste going to landfills. |
| Plastic Bans | Reducing single-use plastics to protect the environment. |
These policies encourage businesses to rethink waste production. They push for more sustainable practices.
Innovations On The Horizon
New technologies are changing how we manage waste. These innovations promise a cleaner future.
- Smart Bins - These bins sort waste automatically.
- Advanced Recycling - New methods turn waste into reusable materials.
- Waste-to-Energy - Converting waste into energy is becoming more efficient.
Smart bins use sensors to identify different types of waste. This helps in proper sorting and recycling.
Advanced recycling breaks down complex materials. It allows more items to be recycled.
Waste-to-energy plants generate power from non-recyclable waste. This reduces landfill use and provides clean energy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is General Waste Management?
General waste management involves the collection, transport, and disposal of everyday waste. It ensures proper handling to prevent pollution and environmental harm. Effective waste management practices include recycling, composting, and landfill use. Proper waste segregation at the source is crucial for efficiency.
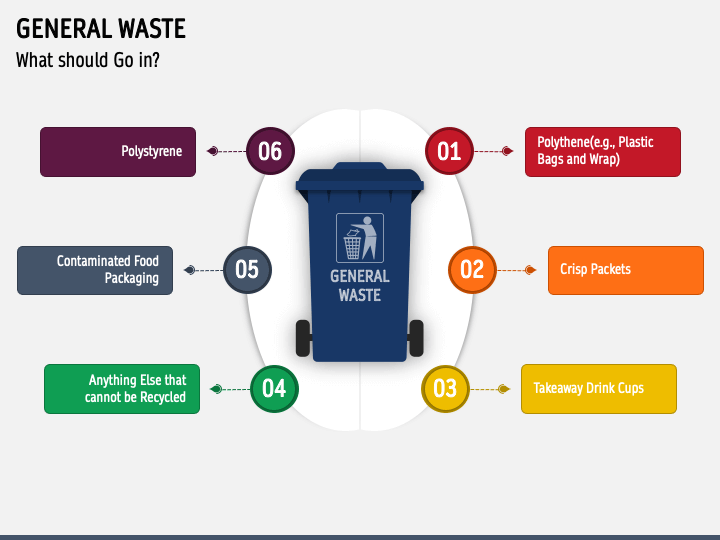
What Does General Waste Include?
General waste includes non-recyclable items like food scraps, plastic wrappers, tissues, and broken household items. These items cannot be composted or recycled.
What Are The Four Types Of Waste Management?
The four types of waste management are recycling, composting, landfilling, and incineration. Recycling converts waste into new products. Composting decomposes organic waste. Landfilling involves burying waste in designated sites. Incineration burns waste to reduce its volume.
What Are The 5 Of Waste Management?
The 5 R’s of waste management are: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Recover, and Residual Management. Reduce waste production. Reuse items. Recycle materials. Recover energy. Manage residual waste properly.
Conclusion
Effective general waste management is crucial for a cleaner environment. Implementing proper disposal methods reduces pollution and conserves resources. Encourage sustainable habits and educate others on waste reduction. Together, we can make a significant impact and ensure a healthier planet for future generations.
Start managing waste responsibly today.