Discover comprehensive insights into liquid waste management in Sydney. This expert guide covers regulations, best practices, recycling, and innovative solutions for residential, commercial, and industrial liquid waste, ensuring a sustainable future for our harbour city.
Get A Quick Quote for liquid waste management.
Under no obligation
1. Introduction: The Criticality of Liquid Waste Management in Sydney
As one of Australia's leading waste management and recycling experts, I can attest to the vital role of effective liquid waste management in maintaining Sydney's environmental health and liveability. From our bustling cityscapes to our pristine waterways, the proper handling of liquid waste is paramount. This article will delve into the complexities of liquid waste management in Sydney, offering a comprehensive overview of current practices, challenges, and the innovative solutions propelling us towards a more sustainable future.
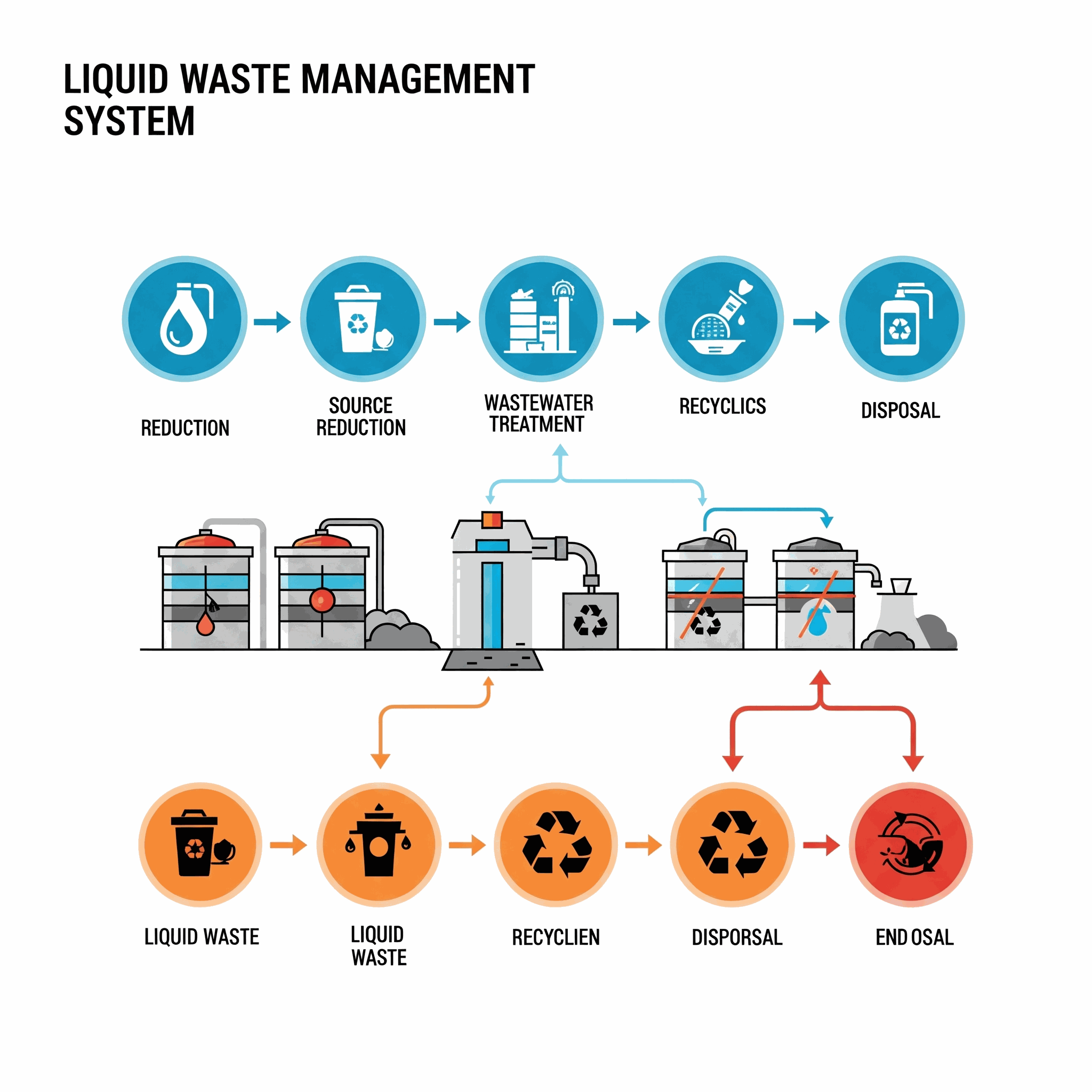
2. What Exactly is Liquid Waste? Defining the Scope
Liquid waste encompasses any waste material that is in a liquid form. This broad category includes a diverse range of substances, from everyday household wastewater to complex industrial effluents. Understanding its various forms is the first step towards effective liquid waste management.
Common types of liquid waste include:
Domestic wastewater: From sinks, showers, toilets, and laundries.
Commercial liquid waste: Grease trap waste from restaurants, car wash runoff, and salon wastewater.
Industrial liquid waste: Chemical solutions, oils, solvents, and process water from manufacturing and industrial operations.
Hazardous liquid waste: Any liquid waste that poses a substantial present or potential hazard to human health or the environment (e.g., certain chemicals, some oils, contaminated water).
3. The Environmental Imperative: Why Proper Liquid Waste Management Matters
Improper disposal of liquid waste can have devastating consequences for Sydney's environment. Untreated or poorly managed liquid waste can lead to:
Water Contamination: Polluting Sydney's rivers, harbours, and coastal waters, harming aquatic ecosystems, and impacting recreational activities.
Soil Degradation: Leaching harmful chemicals into the soil, affecting fertility and potentially contaminating groundwater.
Air Pollution: Volatile organic compounds from certain liquid wastes can evaporate, contributing to air quality issues.
Public Health Risks: Contaminated water can pose serious health threats, leading to waterborne diseases.
Effective liquid waste management is not just an environmental obligation; it's a cornerstone of public health and economic prosperity.
4. Regulatory Framework: Navigating NSW EPA and Sydney Water Guidelines
Sydney operates under a robust regulatory framework designed to ensure responsible liquid waste management. Key bodies include:
NSW Environment Protection Authority (EPA): The primary regulator for waste management in New South Wales, setting guidelines for waste classification, transport, treatment, and disposal, including specific requirements for hazardous and liquid wastes.
Sydney Water: Manages the wastewater network and sets strict requirements for trade wastewater discharge, often requiring businesses to obtain a Trade Wastewater Agreement (TWA) and implement pre-treatment systems like grease traps.
Adherence to these regulations is crucial to avoid hefty fines and environmental damage.
5. Residential Liquid Waste Management: Everyday Actions, Big Impact
While industrial and commercial liquid waste often gets the spotlight, residential practices play a significant role in overall liquid waste management.
Tips for households:
Fats, Oils, and Grease (FOG): Never pour cooking oil or grease down the sink. Collect it in a container and dispose of it in the general waste bin or through specific recycling programs if available.
Chemical Disposal: Utilize local council Household Chemical CleanOut services for paints, solvents, pesticides, and other hazardous household liquids. Never pour them down drains or into stormwater.
Medicines: Return unwanted or expired medicines to pharmacies for safe disposal.
Water Conservation: Reducing overall water consumption directly translates to less wastewater generated.
6. Commercial Liquid Waste Management: Businesses Leading the Way
Commercial enterprises, particularly those in the food service, automotive, and hospitality sectors, are significant generators of liquid waste. Responsible liquid waste management is not only a regulatory requirement but also a mark of good corporate citizenship.
Grease Traps: Essential for restaurants and food businesses to prevent FOG from entering the sewer system. Regular cleaning by licensed contractors is mandated by Sydney Water.
Trade Wastewater Agreements: Many businesses require a TWA from Sydney Water, outlining permissible discharge limits and pre-treatment requirements.
Specialised Services: Utilising licensed liquid waste removal services for specific waste streams like car wash sludge, cooling tower bleed-off, or industrial wash water.
7. Industrial Liquid Waste Management: Complexities and Compliance
Industrial processes often generate complex and varied liquid waste streams, frequently containing hazardous components. Industrial liquid waste management demands specialised expertise and infrastructure.
Waste Characterisation: Thorough analysis to identify the chemical composition and hazard level of the waste.
Pre-treatment Technologies: On-site treatment systems (e.g., pH adjustment, filtration, oil-water separation, dissolved air flotation (DAF) units) to meet discharge criteria.
Licensed Transporters: Engaging EPA-licensed waste transporters for safe and compliant off-site disposal or recycling.
Emergency Response Plans: Robust plans to manage spills and leaks effectively, minimising environmental harm.
8. The Role of Grease Traps: A Sydney Water Requirement
Grease traps are a cornerstone of effective liquid waste management for food businesses in Sydney. These devices prevent fats, oils, and grease from solidifying in sewer pipes, which can cause blockages and overflows. Sydney Water mandates the installation and regular cleaning of grease traps for retail food businesses. Selecting a Wastesafe transporter approved by Sydney Water is crucial for compliance.
9. Trade Wastewater Agreements: Your License to Discharge
For many commercial and industrial operations, a Trade Wastewater Agreement (TWA) with Sydney Water is a legal necessity. This agreement specifies:
Permitted Waste Types: What can and cannot be discharged.
Discharge Limits: Concentration limits for various pollutants (e.g., pH, suspended solids, oils, and greases).
Pre-treatment Requirements: The type of equipment needed to treat wastewater before discharge.
Monitoring and Reporting: Obligations for businesses to monitor their discharge and report to Sydney Water.
Understanding and adhering to your TWA is vital for compliant liquid waste management.
10. The Challenges of Liquid Waste Management in Sydney
Despite advancements, Sydney faces several challenges in liquid waste management:
Growing Population and Urbanisation: Increased waste generation from a rapidly expanding city.
Illegal Dumping: The persistent issue of illicit disposal of liquid waste, often into stormwater drains, leading to severe environmental pollution.
Complex Waste Streams: The diverse and sometimes hazardous nature of industrial and commercial liquid wastes.
Infrastructure Demands: The need for continuous investment in advanced treatment facilities and sewerage networks.
Public Awareness: Bridging the gap in public understanding regarding the proper disposal of household liquid waste.
11. Innovative Solutions in Liquid Waste Treatment
Sydney is embracing innovation in liquid waste management to overcome these challenges.
Advanced Wastewater Treatment Plants: Utilizing technologies like membrane bioreactors (MBRs) and advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) for higher quality effluent.
Resource Recovery from Wastewater: Extracting valuable resources like biosolids (used as fertiliser), energy (biogas), and even purified water for non-potable reuse from wastewater streams.
Smart Sensors and AI: Deploying technologies for real-time monitoring of liquid waste composition and optimizing treatment processes.
Decentralised Treatment Systems: Exploring smaller, localised treatment plants for specific industrial zones to reduce transport costs and burden on centralised facilities.
12. Recycling and Reuse: Closing the Loop on Liquid Waste
The ultimate goal in modern liquid waste management is to move beyond mere disposal to a circular economy model, where liquid waste is viewed as a resource.
Water Recycling: Treating wastewater to a high standard for non-potable uses like irrigation, industrial processes, and even aquifer recharge. Sydney Water is a leader in this area.
Waste Oil Recycling: Reprocessing used lubricating oils into new lubricants or industrial fuels.
FOG-to-Energy: Converting fats, oils, and grease into biodiesel or biogas through anaerobic digestion.
Chemical Recovery: Recovering valuable chemicals from industrial liquid waste streams for reuse in manufacturing.
13. Hazardous Liquid Waste Disposal: A Specialised Process
Hazardous liquid waste requires extreme caution and specialised handling. In Sydney, licensed hazardous waste facilities like those operated by Solveco or REMONDIS Australia provide secure treatment and disposal options. This often involves:
Identification and Classification: Rigorous testing to determine the precise hazardous properties.
Secure Transport: Utilising specialised tankers and trained personnel to prevent spills.
Treatment Technologies: Neutralisation, solidification, incineration (for certain types), or chemical treatment to render the waste less harmful before final disposal.
Documentation: Comprehensive record-keeping of the waste's journey from generation to final disposal.
14. Non-Hazardous Liquid Waste: Everyday Solutions
Even non-hazardous liquid waste, such as septic tank pump-outs, stormwater pit cleanouts, or wash bay water, requires proper management. Companies like Endeavour Liquid Waste and Rapid Vac Trucks Sydney offer services for the collection and disposal of these non-hazardous streams, ensuring they are treated appropriately before discharge to sewer or other approved facilities.
15. Stormwater Management: Preventing Pollution at the Source
Stormwater runoff often carries pollutants from urban surfaces into Sydney's waterways, acting as a form of liquid waste. Effective stormwater management is crucial to prevent this.
Gross Pollutant Traps (GPTs): Devices installed in stormwater drains to capture litter, sediment, and other gross pollutants.
Water Sensitive Urban Design (WSUD): Integrating natural systems like rain gardens and permeable pavements to filter stormwater before it enters waterways.
Community Education: Promoting responsible practices like washing cars on lawns instead of driveways and properly disposing of chemicals.
16. The Role of Technology: Enhancing Efficiency and Compliance
Technology is revolutionising liquid waste management in Sydney.
Automated Monitoring Systems: Real-time data on discharge quality, enabling immediate intervention if limits are exceeded.
GPS Tracking for Waste Transport: Ensuring efficient routing and accountability for liquid waste movements.
Digital Platforms for Waste Tracking: Streamlining documentation and compliance reporting for businesses and regulators.
AI for Waste Sorting and Optimisation: Potentially enhancing the separation and treatment of complex liquid waste mixtures.
17. Case Studies of Success in Sydney
Sydney boasts several examples of successful liquid waste management initiatives:
Sydney Water's biosolids reuse program: Converting wastewater sludge into a valuable agricultural fertiliser, diverting 100% of its biosolids from landfill.
Industrial parks with centralised pre-treatment facilities: Collaborative approaches where multiple businesses share infrastructure for efficient liquid waste treatment.
Local council chemical clean-out events: Providing convenient and safe disposal options for hazardous household liquids, preventing them from entering the general waste stream or drainage systems.
18. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Liquid Waste Management in Sydney
Q1: What are the biggest risks of improper liquid waste disposal?
A1: The biggest risks include severe water and soil contamination, harm to aquatic ecosystems, potential public health issues from contaminated water, and significant legal penalties for non-compliance.
Q2: How often should a commercial grease trap be cleaned in Sydney?
A2: The cleaning frequency for commercial grease traps in Sydney is typically mandated by Sydney Water and depends on the size of the trap and the volume of greasy waste produced. It can range from weekly to monthly or quarterly.
Q3: Can I pour paint down the drain in Sydney?
A3: Absolutely not. Paint is considered hazardous liquid waste and must never be poured down drains or into the stormwater system. It should be disposed of via Household Chemical CleanOut services or specialised waste facilities.
Q4: What is a Trade Wastewater Agreement (TWA)?
A4: A Trade Wastewater Agreement (TWA) is a legal document between a business and Sydney Water that specifies the conditions under which the business can discharge its trade wastewater into the sewer system, including pre-treatment requirements and discharge limits.
Q5: Are there recycling options for liquid waste in Sydney?
A5: Yes, many liquid waste streams can be recycled. This includes used oils, certain chemicals, and treated wastewater for non-potable reuse. Dedicated facilities and services exist for these purposes.
19. The Community's Role: A Shared Responsibility
Effective liquid waste management is not solely the responsibility of industries and government agencies. Every individual in Sydney has a role to play:
Educate Yourself: Understand what constitutes liquid waste and how to dispose of it correctly.
Support Sustainable Businesses: Choose businesses that demonstrate responsible waste management practices.
Report Illegal Dumping: Be vigilant and report any instances of illegal liquid waste disposal to the relevant authorities (e.g., EPA, local council).
Conserve Water: Reducing water usage directly lessens the volume of wastewater that needs treatment.
20. Conclusion: Towards a Greener, Cleaner Sydney
Liquid waste management in Sydney is a complex yet crucial endeavour. As an expert in this field, I believe Sydney is on a promising trajectory towards more sustainable practices, driven by robust regulations, innovative technologies, and a growing commitment to resource recovery. By understanding the challenges and embracing best practices, we can collectively ensure that our harbour city remains a beacon of environmental stewardship for generations to come.
Call to Action
Ready to enhance your liquid waste management practices in Sydney? Whether you're a homeowner, business, or industry, understanding and acting on these insights is vital. Contact a reputable, EPA-licensed liquid waste management provider today for a tailored assessment and solution that benefits both your operations and our precious environment. Let's work together to make Sydney's future cleaner and greener